What is spermidine?
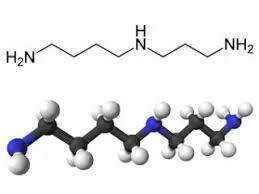
Spermidine is an organic compound that belongs to the group of polyamines and is naturally produced in the body. It has a major role in various cellular processes, such as gene expression, cell proliferation, and apoptosis1.
Autophagy, which can be defined as the process of degradation and recycling of cellular components within cells2, is also influenced by spermidine.
Spermidine is available from certain food sources, such as sesame seeds, wheat germ, legumes, mushrooms and whole grains3. It can also be synthesized in the laboratory from putrescine – another natural polyamine4. Researchers have demonstrated that spermidine plays diverse roles in different biological processes5.
In particular, spermidine promotes autophagy activity through its ability to bind to proteins involved in autophagy6. By doing this spermidine can induce autophagic flux7 – a process wherein damaged organelles and macromolecules are degraded for recycling8. In addition, spermidine also upregulates autophagosome formation9 – which increases autophagic flux10 – by increasing levels of key proteins involved in autophagosome formation11 .
Studies conducted on spermidine-treated animal models indicate that spermidine supplementations can reduce inflammation12 and improve metabolic health13. There are several clinical studies underway to assess whether spermidine supplementation could be beneficial for human health14.
These studies suggest that spermidine-induced autophagy may provide therapeutic benefits15 and could pave way for potential treatments for age-related diseases16.
What are the benefits and side effects of spermidine supplements compared to food?
Spermidine is a polyamine that has been gaining significant attention due to its potential to treat age-related diseases and reduce inflammation. Research has shown spermidine supplementation may provide numerous benefits such as improving cardiovascular health, lowering blood pressure, increasing appetite control, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, and even activating autophagy. Autophagy is an important cellular process in which damaged cellular components are recycled by the body.
Some of spermidine’s most studied benefits come from its ability to stimulate autophagy. Autophagy can help maintain healthy cells, clear out debris, and remove damaged or aging cells. This process can help prevent some chronic illnesses like cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. It can also help keep the heart healthy by clearing out damaged cholesterol particles and preventing plaque build-up in artery walls. Additionally, spermidine may also promote healthier skin and hair by preventing free radical damage in the skin cells.
The best way to get spermidine into your body is through food sources like wheat germ, soybeans, mushrooms, legumes, whole grains and nuts. While spermidine naturally occurs in these foods, supplementing with spermidine could increase spermidine levels more effectively than just eating these foods alone. However, it is important to note that spermidine supplements are not regulated or standardized by any governing bodies so they may contain potentially dangerous or ineffective ingredients if purchased from untrustworthy sources.
Although spermidine supplements have been found to be generally safe for most people when taken at certain dosages for short periods of time there are a few side effects that have been reported such as nausea, headache, fatigue and dizziness but these symptoms usually go away after discontinuing spermidine supplementation. Additionally long-term studies have not been conducted yet so it is unclear if there would be any long-term health risks associated with spermidine supplement use but more research is needed before this can be determined conclusively.
In conclusion spermidine found in food sources appears to be beneficial in providing cellular protection against disease while spermidinesupplements may offer additional benefits that could outweigh any potential risks or side effects depending on individual needs. As always it’s best to consult your healthcare provider before starting any type of dietary supplement regimen including spermidinesupplements since everyone’s situation is unique and what might work for one person might not work for another person.
Does spermidine induce autophagy?
Spermidine is a natural polyamine compound found in organisms ranging from microorganisms to humans, and has been suggested as a potential inducer of autophagy. Autophagy is an evolutionary conserved process that involves the degradation and recycling of cellular components and has been shown to play important roles in health and disease.
Studies have revealed that spermidine is able to activate protein kinases, such as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), leading to an increase in the levels of sirtuins as well as other factors involved in autophagic pathways. In addition, spermidine was demonstrated to enhance lysosomal biogenesis by increases in lysosomal proteolytic enzymes, which are essential for proper autophagosome formation and function. Furthermore, spermidine was also found to decrease the levels of mTOR facilitating autophagy induction.
In conclusion, spermidine can indeed induce autophagy through multiple signaling pathways including AMPK/sirtuin activation, lysosomal biogenesis enhancement, and mTOR inhibition. This makes spermidine an attractive target for future research as a potential intervention for disorders related to dysregulation of autophagy such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
How do I know if I’m in autophagy?
Autophagy is a process by which your cells eliminate old and damaged components, such as proteins, lipids, and organelles. spermidine has been shown to increase autophagy in many different cell types. It is an important part of cellular health and allows the body to maintain its youthful state.
The most common way to assess autophagy levels is through fluorescence microscopy. Cells that are undergoing autophagic activity will have increased levels of various markers associated with autophagy. spermidine can be used as a marker when assessing cell health via fluorescence microscopy. spermidine also increases the intracellular lysosomal pH, which further increases the efficiency of the autophagic process.
Another way to assess autophagy levels is by measuring spermidine concentrations in the cell. spermidine is known to promote autophagic flux through its pro-autophagic effects on both macroautophagy and microautophagy pathways. Thus, spermidine concentrations can be used as an indicator of a cellular environment that is favorable for autophagic activity.
If you are interested in assessing your own cells for autophagic activity, you can use spermidine in combination with other markers to measure autophagy levels in your cells over time. By measuring spermidine concentrations before and at different time points after treatment with spermidine, you can determine if your cells are undergoing increased autophagic activity or not.
Additionally, spermidine can help you identify which types of nutrients or drugs may be beneficial in promoting healthy cellular functioning and promoting longevity through increased autophag yactivity.
Spermidine, an autophagy inducer, as a therapeutic strategy in neurological disorders
Spermidine is a polyamine compound found naturally in all living organisms, including humans. In recent years, spermidine has been found to induce autophagy, a natural process by which cells clean out damaged or unwanted cellular components. Autophagy plays an important role in maintaining cellular health and plays a critical role in disease prevention and treatment, especially when it comes to neurological conditions.
It has been suggested that spermidine may act as an autophagy inducer to help treat some neurological disorders. The exact mechanism behind this potential therapeutic strategy is still being studied; however, spermidine has been linked to the stimulation of lysosome activity and increased production of autophagosomes – structures necessary for autophagic degradation.
Spermidine has also been reported as having neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress and apoptosis-related cell death.
Research suggests spermidine could be used as a therapeutic agent for many neurological disorders, including brain cancer, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), stroke, Alzheimer’s disease and traumatic brain injury. Studies conducted on animal models have shown spermidine supplementation is able to reduce the progression of these diseases by decreasing inflammation and promoting nerve cell survival.
In addition to its potential as an autophagy inducer, spermidine offers other benefits that are relevant to neurological health. It helps maintain healthy levels of cholesterol and other fat molecules in the body while providing antioxidant protection against free radicals – unstable molecules that have been linked to cognitive decline associated with aging. Moreover, spermidine can help protect nerve cells from oxidative stress-induced damage which can lead to synaptic dysfunction and memory loss associated with Alzheimer’s disease progression.
Overall, spermidine appears to be an effective therapeutic strategy against certain neurological disorders due to its ability to stimulate autophagy while providing other beneficial effects such as antioxidant protection and cholesterol management. More research into spermidines impact on autophagy induction is still needed but current studies suggest this compound could offer a promising new therapeutic option for various neurological diseases or disorders.