Secondary hypogonadism is a condition in which the testes do not produce sufficient levels of testosterone due to a lack of stimulation from other systems. Recently there has been a plague of secondary hypogonadism that is affecting men at a younger age each year. The most common symptom of secondary hypogonadism is low libido and energy levels, but it can also lead to depression, muscle loss, and fat gain. In addition, secondary hypogonadism can cause brain fog, reduced drive and motivation, and decreased satisfaction with life. If you think you may be suffering from secondary hypogonadism, it is important to speak to an experienced clinician. While there is no cure for the condition, there are treatments that can help to eliminate your symptoms and optimize your hormonal profile.
What are the causes of secondary hypogonadism?
Low testosterone due to secondary hypogonadism has many causes, making it an extremely complex problem for men trying to find relief. The modern environment makes hormonal regulation extremely difficult, because there are so many factors concurrently having a negative impact. The central nervous and neuroendocrine systems are primarily responsible for failure in the context of secondary hypogonadism, and societal influences and environmental factors even have an impact on function. For example, exposure to endocrine disruptors, like xenoestrogens found in plastics, can interfere with hormone production and lead to secondary hypogonadism. Xenoestrogens such as parabens and Bisphenol A (BPA) are commonly found in many everyday items, from cosmetics to food packaging.
Additionally, sedentary lifestyles and certain medications can also cause the body to produce less testosterone. While societal and environmental factors may seem out of our control, there are steps we can take to protect ourselves from endocrine disruptors. By reducing our exposure to single-use plastic we lower our intake of microplastics. It is also important to make informed choices about what household products you choose as many of these products contain harmful endocrine disruptors.
How is secondary hypogonadism treated?
Secondary hypogonadism is a condition that causes low testosterone in men, and in recent years it has become the most common cause of low testosterone in young men. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are responsible for regulating the level of circulating sex hormones in the body (testosterone and estrogen), and any disruption in the function of these organs can result in hormonal dysregulation. There are several excellent treatment options for secondary hypogonadism, which is typically treated with clomiphene citrate, enclomiphene citrate, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), or gonadorelin.
Clomiphene citrate, enclomiphene citrate and gonadorelin are medications that help to stimulate the release of gonadotropins from the pituitary gland. On the other hand, HCG is a hormone that helps to stimulate the production of testosterone by the testes. Gonadorelin is a medication that helps to stimulate the release of gonadotropins from the pituitary gland. Testosterone is a hormone that helps to stimulate the development of male sexual characteristics.
What are the consequences of untreated secondary hypogonadism?
Left untreated, secondary hypogonadism can have many serious consequences. For men, these can include weight gain, erectile dysfunction, impotency, infertility, decreased libido, muscle loss, depression and loss of life satisfaction. Additionally, untreated hypogonadism can increase the risk of developing diabetes and other chronic health conditions. With so much at stake, it is essential that anyone experiencing symptoms of secondary hypogonadism seek treatment from a qualified healthcare provider.
How can you prevent secondary hypogonadism?
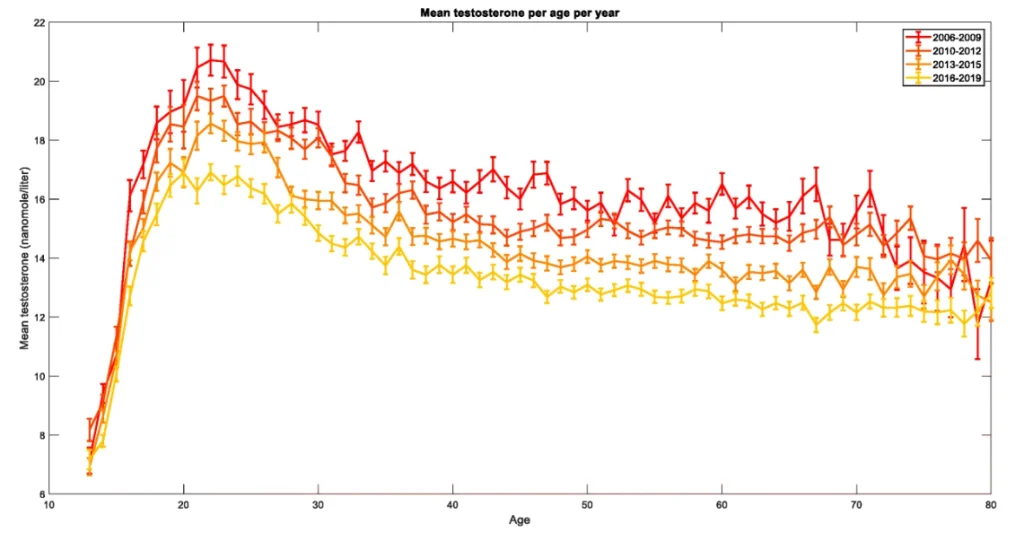
Secondary hypogonadism is a condition in which the testes don’t produce enough testosterone. It can be caused by a wide variety of factors such as stress, sedentary lifestyle, lack of sleep, diet, social influences, exposure to xenoestrogens, and societal pressures. There are such a variety of factors applying negative pressure to this system that men today have become obsessive about raising their testosterone levels, and have had very little positive effect in doing so. It seems that despite the obsession and extreme measures that men are going through, the plague of secondary hypogonadism is becoming increasingly prevalent.
While it is true that the best way to prevent secondary hypogonadism is to manage stress, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and get enough sleep; it is near impossible to avoid the societal influences, microplastics and plethora of environmental factors contributing to this issue without becoming a reclusive monk that is withdrawn from modern society.
Secondary hypogonadism is a real condition that affects far more men today than ever before, one which too often goes untreated. It can have profound effects on men’s physical, mental, and emotional health -but the good news is that it is treatable. If you think you might be suffering from secondary hypogonadism, reach out to the clinical team at Valhalla Vitality. We are here to support you in taking charge of your health and happiness.
Works Cited
- Chodick, Gabriel & Epstein, Shdema & Shalev, Varda. (2020). Secular trends in testosterone- findings from a large state-mandate care provider. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology. 18. 10.1186/s12958-020-00575-2.
- Zilioli, S., & Watson, N. V. (2014). Testosterone across successive competitions: evidence for a ‘winner effect’ in humans?. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 47, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.05.001
- Endocrine disruptors. (2022). Retrieved from https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/agents/endocrine/index.cfm
- Kumar, P., Kumar, N., Thakur, D. S., & Patidar, A. (2010). Male hypogonadism: Symptoms and treatment. Journal of advanced pharmaceutical technology & research, 1(3), 297–301. https://doi.org/10.4103/0110-5558.72420
- Carnegie C. (2004). Diagnosis of hypogonadism: clinical assessments and laboratory tests. Reviews in urology, 6 Suppl 6(Suppl 6), S3–S8.






