The following blog post is for entertainment and informational purposes only. It is not intended to provide medical advice or diagnosis. Please consult your doctor before making any health-related decisions.
Rapid skin cell turnover causing red and scaly patches can negatively affect quality of life. Topical therapies, phototherapy, and systemic medicines provide some relief. However, they can cause side effects or limitations. A recent promising option for treating psoriasis Rapamycin is known for its immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory properties.
Now we will introduce to you the possible advantages, mechanics, and current research of the use of the Rapamycin psoriasis effects in addressing this condition.
Rapamycin was initially designed to prevent organ transplant rejection because it inhibits mTOR. This protein kinase actively participates in regulating cell growth, proliferation, and immune responses. The capacity of the drug to modulate these pathways can offer both anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative effects. This ability makes it an eligible treatment alternative for psoriasis.
Possibility of Rapamycin Psoriasis Cure
The ability of this compound to impact multiple cellular and molecular mechanisms shows great potential in treating psoriasis. A better comprehension of these action mechanics sheds light on the ways of the operation. Rapamycin psoriasis effect can offer relief for this long-term autoimmune ailment.

Oppression of the mTOR Pathway
The main function of the compound is to obstruct the activity of mTOR. This allows for managing cell development, spreading, and metabolism.
1. Regulation of Keratinocyte Spreading
The characteristic trait of psoriasis is presented by the speedy growth of keratinocytes. They provide the development of rough and flaky patches. mTOR signaling controls cell expansion and division. Rapamycin psoriasis action obstructs mTOR to restore regularity in keratinocyte spreading and decreases surplus in individuals with psoriasis.
2. Cell Cycle Control
By regulating crucial checkpoints and promoting the progression of the cell cycle, mTOR exerts influence on it. Rapamycin psoriasis action inhibits mTOR’s functions. So, the compound decelerates the rate of division of the cells. As a result, the keratinocytes’ fast-paced spreading is reduced.
Modulating Immune Reactions
Inflammatory processes in psoriasis are resulted from an exaggerated immune reaction using T cells and other immune cells.
1. T Cell Suppression
Rapamycin psoriasis action is capable of immunosuppression through the regulation of T cell activation and proliferation. By disrupting signaling pathways essential for their development and operation, it effectively restrains the activation process in these cells. This feature enables the compound to decrease excessive activity among T cells that fuel inflammation as well as immune irregularities associated with psoriasis.
2. Cytokine Production
The pro-inflammatory cytokines incite inflammatory processes in psoriasis. Their production is reduced by Rapamycin. Such signaling molecules play a prominent role in the disorder’s pathogenesis. By curbing their release, the compound effectively alleviates inflammatory reactions and enhances skin condition.
3. Lowering Inflammatory Effects
Psoriasis triggers the inflammatory process through immune cells and cytokines. They incite perpetual inflammatory processes and cause tissue injury.
Rapamycin psoriasis action impacts multiple downstream signal pathways for inflammatory processes. Its manipulation of these pathways results in decreased skin inflammation. This action reduces redness, swelling, and discomfort of the condition.
Suppression of the overly active immune response by the Rapamycin psoriasis effect helps to reestablish equilibrium within the immune system. This regulation of immunological function mitigates autoimmune action and influences the onset and continuation of symptoms of psoriasis.
Skin Benefits of Rapamycin Psoriasis Cure

1. Enhancing Skin Barrier Functionality
The symptoms of psoriasis can worsen due to a compromised skin barrier because it permits the entry of irritants and pathogens into the skin.
2. Improving Skin Restoration
Regulation of the development and differentiation of cells by Rapamycin psoriasis action provides the possibility to aid skin restoration processes. This can result in a more robust skin barrier and harm from external factors. So, this leads to an enhancement in general skin health.
3. Reducing Skin Cell Turnover
Rapamycin psoriasis action assists in regulating skin cell turnover by managing the reproduction of keratinocytes. This lessening of superfluous cell generation plays a role in improving psoriasis plaques and reinstating a healthier, more balanced complexion.
The reason for the potential of this compound in treating psoriasis relates to its versatile modes of action. It sets the pace by blocking the mTOR pathway, thereby regulating keratinocyte growth and densities while curtailing inflammatory and immune reactions. Additionally, it intensifies skin barrier function resulting in lower symptoms of psoriasis as well as improved overall health of your skin. Despite being a promising solution for managing psoriasis; further research is crucially needed to confirm both effectiveness plus safety among patients undergoing clinical treatments using this medication approach significantly though still requires extensive exploration of efficacy outcomes.
Current Research and Evidence: Link Between Potential of Rapamycin and Psoriasis Cure
Studies conducted recently have investigated the effectiveness of Rapamycin for curing psoriasis, displaying encouraging outcomes.
The effectiveness of topical Rapamycin psoriasis cure formulations has been assessed through clinical trials. Early findings indicate that the application of this medication can decrease the severity of psoriasis plaques while enhancing skin appearance, with negligible adverse effects on bodily systems.
Although research on the connection between the abilities of Rapamycin and psoriasis healing is still in its early stages, there are indications that its immunosuppressive effects could provide a new method of treatment for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis who have not experienced success with traditional therapies.
The attention of some studies has turned to pairing the Rapamycin psoriasis effect with additional methods of treating this condition in order to improve its overall effectiveness. The combination of Rapamycin and psoriasis treatments could result in synergistic benefits, resulting in improved management of the symptoms of this condition.
Advantages of Rapamycin for Psoriatic Arthritis Cure
The capacity of the medicine to lessen inflammatory processes and regulate immune responses can decelerate joint damage’s advancement. It can impede additional deterioration of joint structures and preserve their functionality.
The swelling and pain associated with PsA stem from inflammatory processes in the lining of joints. Rapamycin psoriatic arthritis cure can decrease this event. So, it promotes better joint health and mobility.
Treating skin symptoms can also yield advantages as psoriatic arthritis frequently accompanies psoriasis. The impact of the compound on the mTOR pathway can diminish excessive skin cell growth in psoriasis and PsA. Through enhancing dermatological outcomes, the compound provides a twofold advantage for individuals suffering from both conditions.
Better management of psoriasis plaques and an improvement in overall symptom relief, resulting from enhanced skin health, can positively impact the patient’s quality of life.
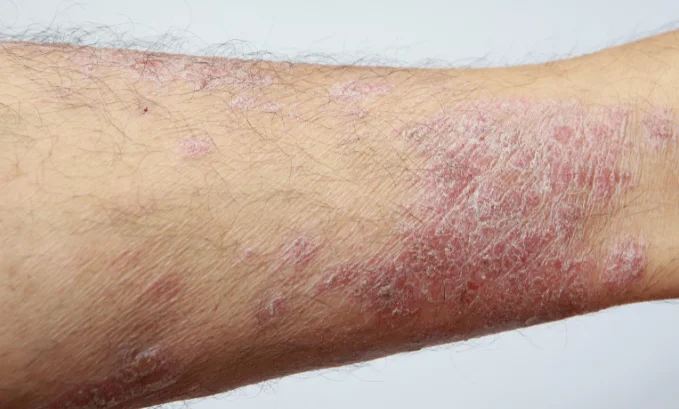
Potential for Combination Therapy
The efficacy of the Rapamycin psoriatic arthritis cure can be advanced in combination with other treatments. Adding other drugs or biologics to the compound intake determines a more inclusive strategy for managing this condition. This approach holds the potential to yield superior management over both skin symptoms and joint inflammation.
The integration of the compound into a customized treatment regimen enables the precise targeting of PsA-related pathways. This provides the possibility to advance results and reduce adverse reactions.

Rapamycin psoriatic arthritis cure by targeting the mTOR pathway promotes reduced inflammatory processes, modulated immunity responses, and slowed disease progression. Patients with concurrent psoriasis can also benefit from its impact on skin symptoms. However, more research and clinical trials are needed to fully establish the efficacy and safety of Rapamycin psoriatic arthritis management. So, people are advised to work closely with their medical service professionals. They help to determine the suitability of the approach to their individual needs.
The potential of the Rapamycin psoriasis cure is provided by its ability to manipulate key pathways of the disease’s progression. Its impact on the mTOR pathway allows it to address both excessive skin cell growth and inflammatory processes at their source. This healing effect presents an exciting new option for managing this condition. However, while initial research has shown great promise, further studies are necessary before determining optimal usage guidelines and safety risks for patients with psoriasis. As our understanding of how best to utilize Rapamycin psoriasis cure continues evolving over time; we may find that it becomes a valuable addition in successfully tackling this challenging ailment alongside other established treatments currently available.






