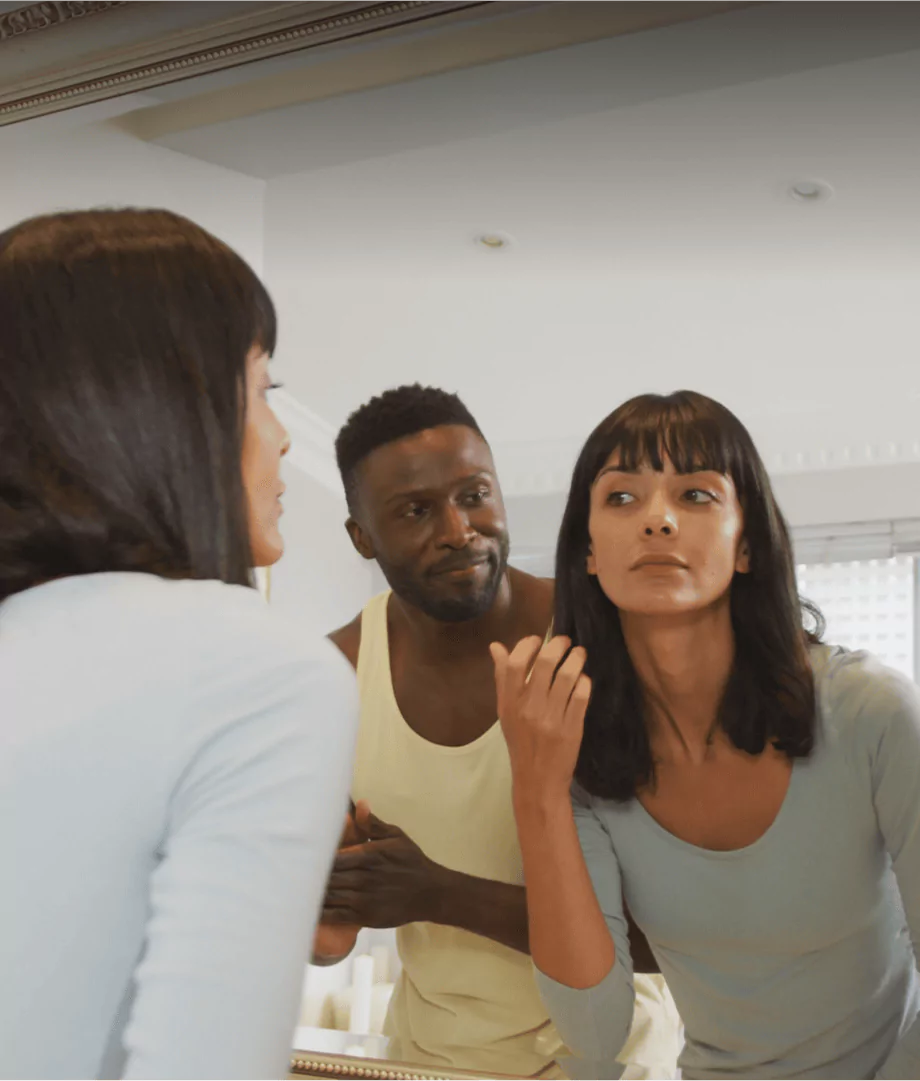
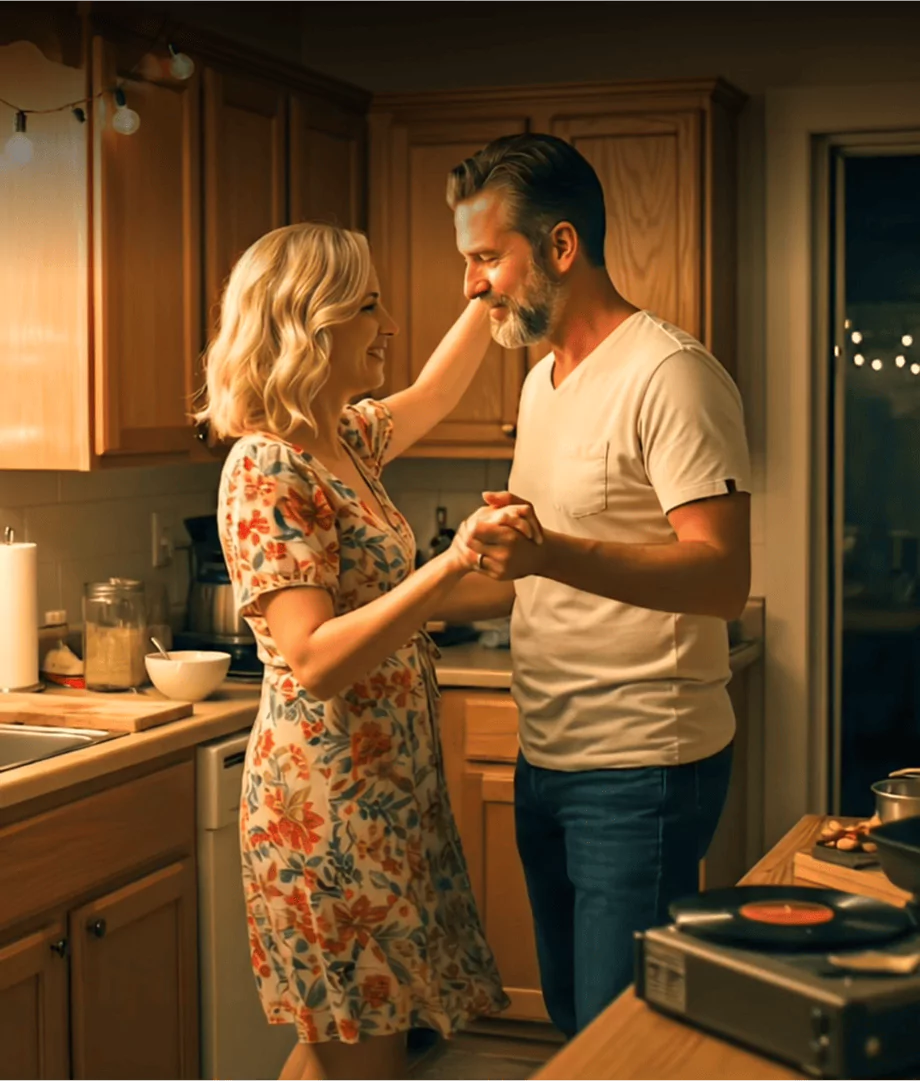
A New Era of Personalized Wellness
The future of care, reimagined. Provider-led, Powered by AI, Designed to grow with you.
Start Your Wellness JourneyYour Personalized Care Network
Everything you need for personalized healthcare in one integrated platform
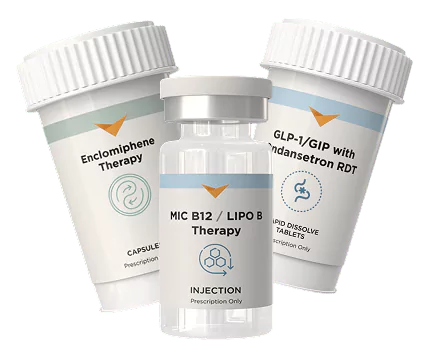
Explore Therapies
Comprehensive treatment options tailored to your unique wellness goals
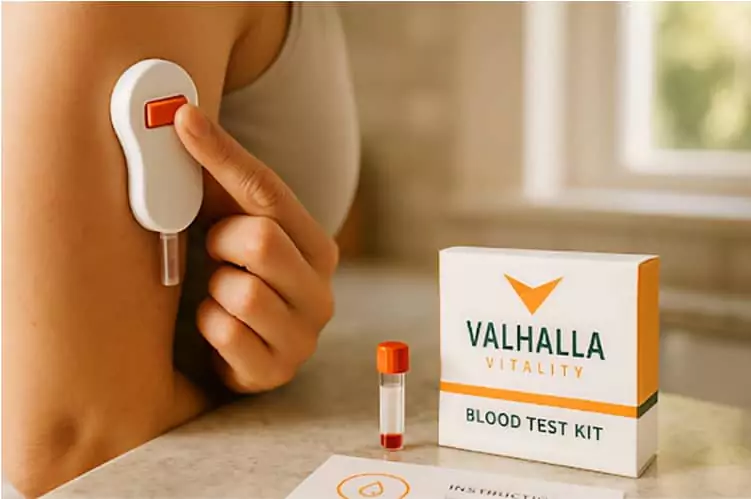
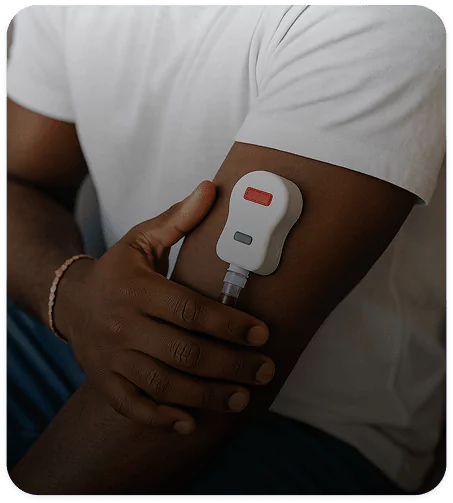
Get Clarity From Day One
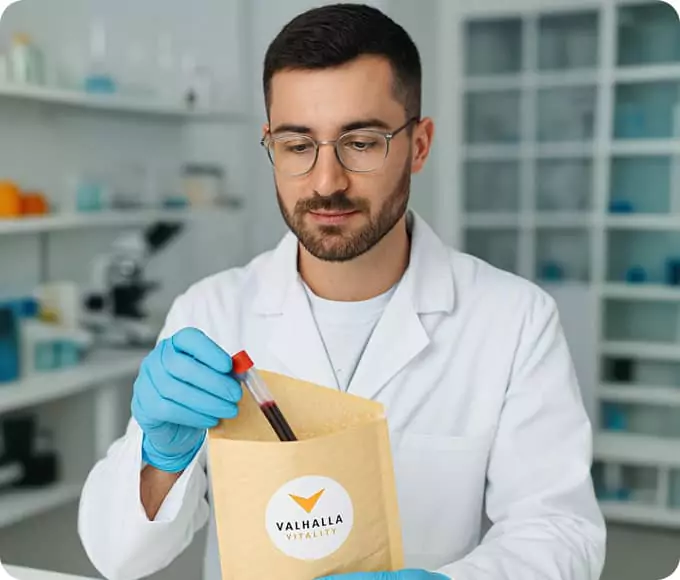
Start your journey with convenient, painless at-home labs. No waiting rooms, just results that empower your provider-guided plan.Choose from tests like the Comprehensive Wellness Panel, Hormone Panel, and Female Wellness Panel.
-
At-Home
Convenient testing
-
Fast Results
Quick turnaround
-
Comprehensive
Full health picture
-
Actionable
Clear next steps
The Vitality Nexus: Smarter Tools. Better Support.
The Vitality Nexus brings together AI-guided tools and real people to support you at every step. From your plan to your progress, you’re backed by smart systems and human care, always.
-
 Start My Wellness Blueprint
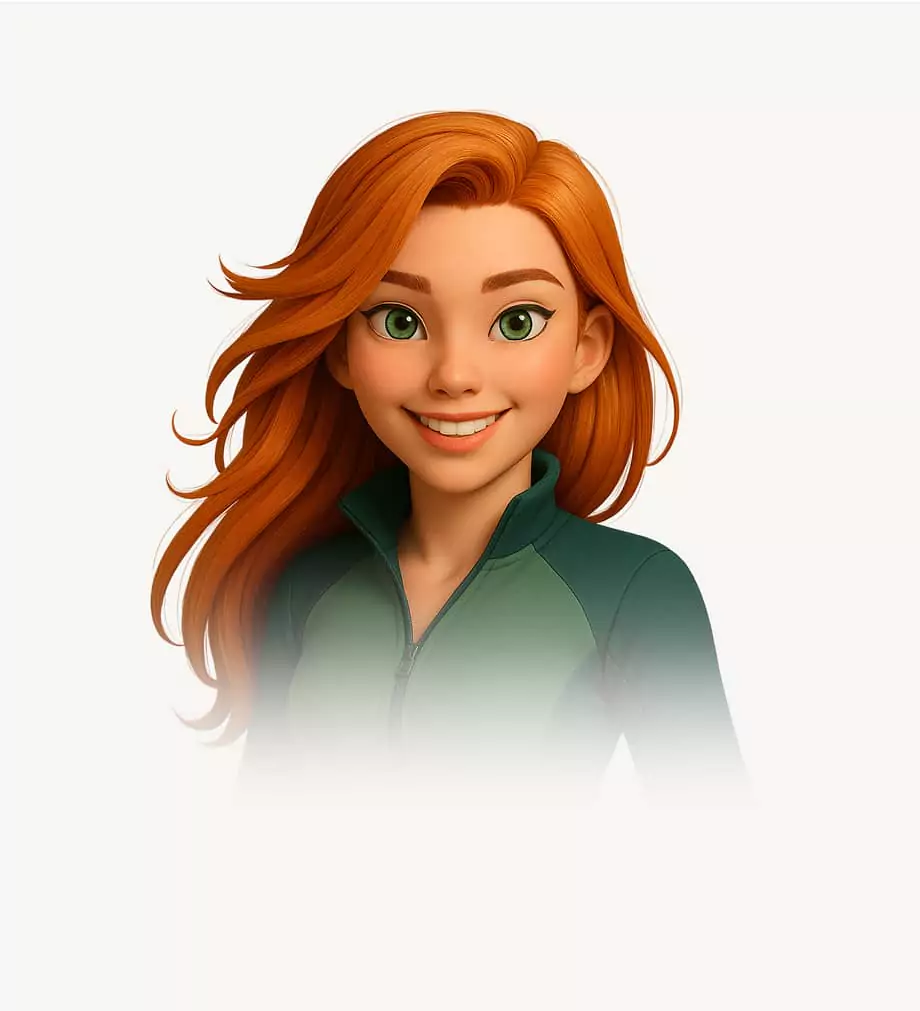
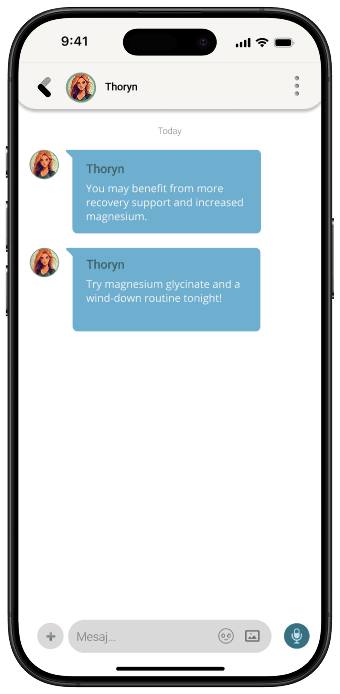
Start My Wellness BlueprintThoryn
Hey I’m Thoryn, your personal AI Wellness Coach. I help track your progress, and build a wellness blueprint that evolves with you. I work alongside your provider to fine-tune treatments, offer proactive guidance, and support your long-term wellness goals
-

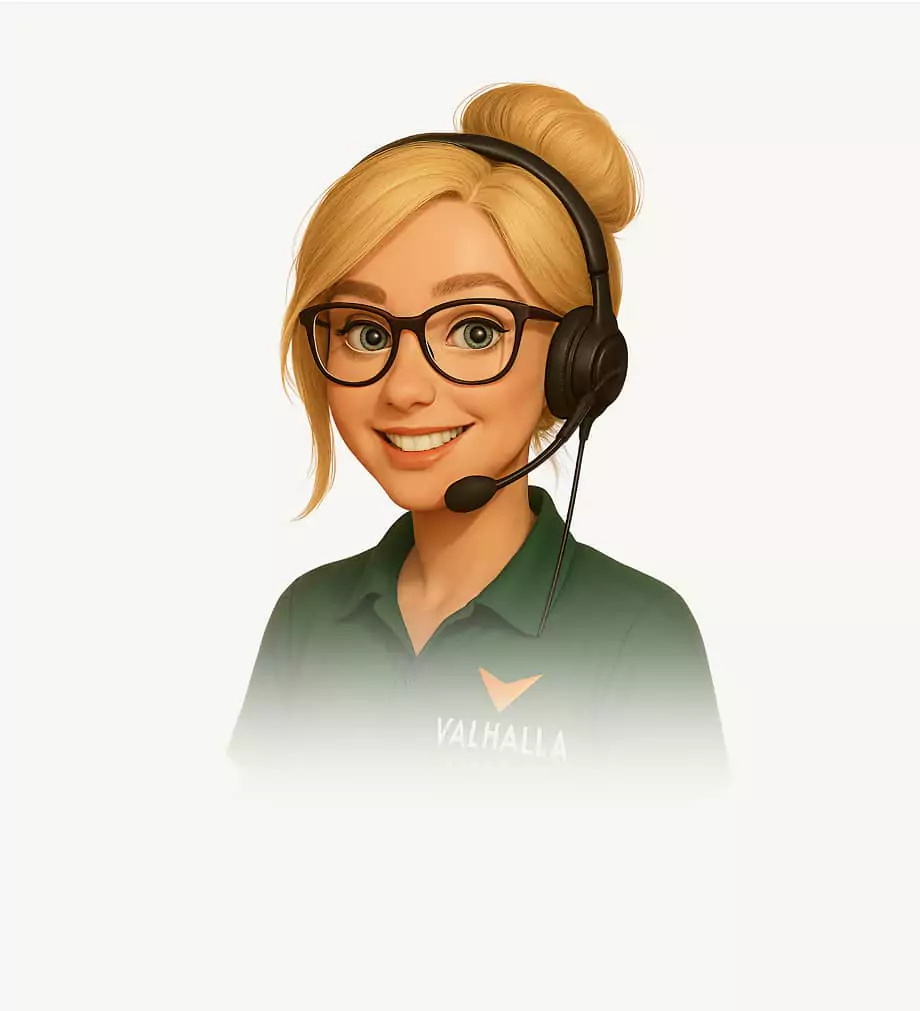
Astrid
Hi, I’m Astrid, your Vitality Ambassador. I’m here to help you feel confident and supported as you move through your wellness journey. From account questions to scheduling support, I make sure you always know where to go and what comes next.
How Our AI Transforms Your Care
We don't just use AI for convenience, we use it to personalize, protect, and continuously improve your care. Every lab result, check-in, and therapy decision is part of a smarter care loop that adapts to you.

Data-Driven Labs
We start with real diagnostic insights from your at-home lab kits.

AI + Provider Collaboration
Thoryn and your provider work together to interpret your data, personalize your therapy, and make proactive adjustments as your needs evolve.

Smart Monitoring & Adjustments
You'll get real-time tracking, milestone nudges, and plan refinements — all informed by your ongoing progress.

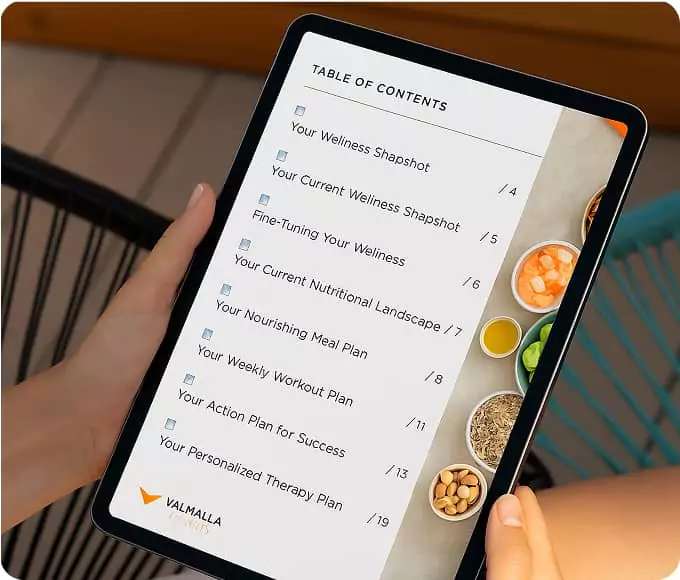
Your Personalized Vitality Blueprint
Thoryn uses your health goals and lab results to generate a dynamic plan. Your provider refines it. Together, they guide your personalized therapies, nutrition, and long-term wellness path.
How It Works
A smarter wellness journey, powered by data, guided by providers, and made personal with AI.
Get Your Vitality Blueprint
Hi, I'm Astrid, I'll walk you through registration ! Receive your Wellness Blueprint to help with your wellness goals.
Order Therapy
Start a personalized treatment plan tailored to your health goals, preferences, and progress — compounded just for you.
Answer Questions in Vitality Nexus
Collaborate with your AI assistant and provider in real time to fine-tune your plan. Receive updates, guidance, and proactive adjustments to keep you on track.
Receive Your Therapy
Track your milestones, get smart check-ins, and earn points as you move forward — every step supported and optimized for results.
The Power Behind Your Progress
Your personalized wellness plan, powered by labs, AI, and real-time insights. From your first lab to your custom therapy, each step is informed by diagnostics and refined by our AI. Providers lead the way — Thoryn helps your care evolve with precision and speed
Earn More As You Grow
Our VIP rewards program grows with your wellness journey
-

Bronze
(500 VIP Points)
Bronze
(500 VIP Points)
- 1% off all purchases
- 1 point per $1 spent
- 500 birthday bonus points
- Access to exclusive promotions
-

Silver Tier
(1000 VIP Points)
Silver Tier
(1000 VIP Points)
- 2% off all purchases
- All Bronze perks included
-

Gold Tier
(2500 VIP Points)
Gold Tier
(2500 VIP Points)
- 5% off all purchases
- All Silver perks included
-

Platinum Tier
(5000 VIP Points)
Gold Tier
(2500 VIP Points)
- 10% off all purchases
- All Gold perks included
Points expire after 12 months. Minimum redemption: 500 points (50 points = $1). Rewards can be applied at checkout.
-
1 Point Per $1 Spent
Earn rewards on every purchase
-
500 Points Per Referral
Share the wellness and earn big
-
Exclusive Benefits
Unlock perks as you level up

Individual results may vary. Testimonials reflect personal experiences and may not represent typical outcomes

I consent to Valhalla Vitality using my review and any uploaded photo on its website and marketing materials

Are you a licensed provider?
Join our national care network.
Partner with Valhalla Vitality to deliver cutting-edge wellness solutions with AI-powered support and comprehensive patient care tools.
-
National Network
Coast-to-coast reach
-
Patient-Centered
Focus on outcomes
-
Excellence
Quality standards
-
Growth
Expand your practice
Your Personalized Wellness Starts Here
Join thousands who've transformed their health with our provider-guided, AI-powered platform.
Start Your Wellness JourneyEligibility and treatment determined after provider consultation. Compounded medications only.